This theory was first proposed in 1905 by Konstantin Mereschkowsky a Russian biologist in his article The nature and origin of chromatophores in the plant kingdom. The endosymbiotic theory explains how organelles inside eukaryotic cells are descended from ancient.

8 16d Endosymbiotic Theory And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts
The endosymbiotic theory refers to the organelles mitochondria and plastids plastids refer to chloroplasts chromoplasts and gerontoplasts to name a few however mainly focuses on chloroplasts.
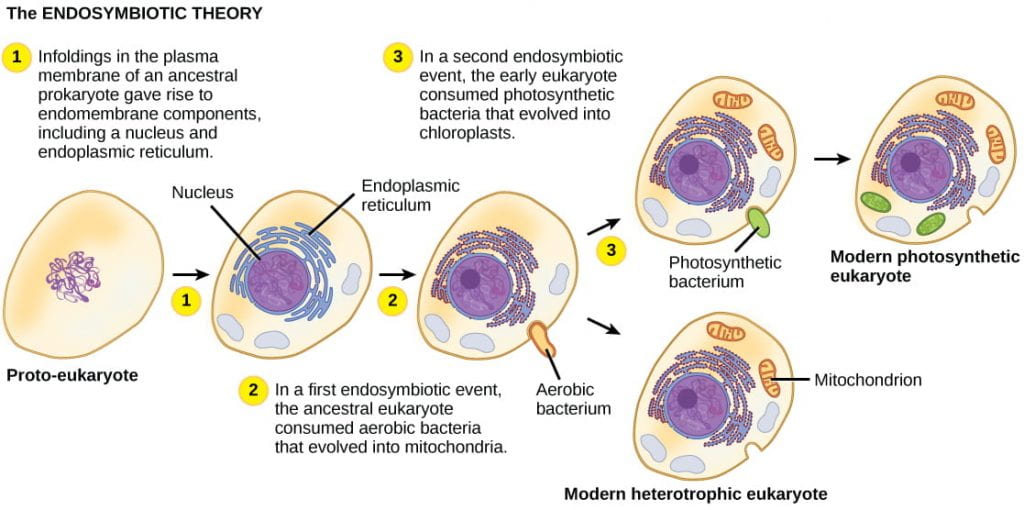
. Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was nominated by the American evolutionist biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. It also indicates that we all have formed from common ancestor. Theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic cells.
The endosymbiotic event that generated mitochondria must have happened early in the history of eukaryotes because all eukaryotes have them. For over 100 years endosymbiotic theories have figured in thoughts about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. First proposed by Boston University biologist Lynn Margulis in the late 1960s the Endosymbiont Theory proposed that the main organelles of the eukaryotic cells were actually primitive prokaryotic cells that had been engulfed by a different bigger prokaryotic cell.
Wihac oin it lest three. More than 20 different versions of endosymbiotic theory have been presented in the literature to explain the origin of eukaryotes and their mitochondria. It was not easy and he was repeatedly denied his publication because at that time he dominated the idea that eukaryotes were the result of gradual changes in the.
For over 100 years endosymbiotic theories have figured in thoughts about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Then later a similar event brought chloroplasts into some eukaryotic cells creating the lineage that led to plants. The defining characteristic of eucaryotic cells is that they contain membrane-bound cell organs and a true karyon.
More than 20 different versions of endosymbiotic theory have been presented in the literature to explain the origin of eukaryotes and their mitochondria. Endosymbiotic theory explains the evolution of mitochondria and chloroplast in eukaryotic cell. Evidence to support the endosymbiotic theory 17-2 428-429 1 mitochondrial DNA and chloroplasts contain DNA similiar to bacterial DNA 2 mitochondria and chloroplasts have ribosomes whose size and structure closely resemble those of bacteria3 like.
Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is an evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms first articulated in 1905 and. The endosymbiotic theory is based upon the thought that eucaryotic cells evolved in stairss get downing with the stable incorporation of chemo-organotrophic and phototrophic symbionts from the sphere bacterium. The dividing of mitochondria already present in the cell.
The endosymbiotic theory history. The Endosymbiotic hypothesis is one of the oldest evolutionary hypotheses still in use today. The major reason for these two organelles being involved in the endosymbiotic theory is because they both contain a small genome.
The role of energy. It says that a prototypic nucleated eukaryotic cell obtained both the mitochondria and the chloroplast from engulfing prokaryotes capable of oxidative phosphorylation and photosynthesis respectively. Ecology The theory that concerns the origins of mitochondria and chloroplasts which are organelles of.
The endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells states that all the individuals are evolved from the same individual. Very few of those models account for eukaryotic anaerobes. Endosymbiotic theory suggests that the eukaryotic cells organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved as a result of early endosymbiosis between prokaryotic endosymbionts and the eukaryotic host cell.
Where he proposed that plastid or. This prototypic eukaryotic cell then evolved. Very few of those models account for eukaryotic anaerobes.
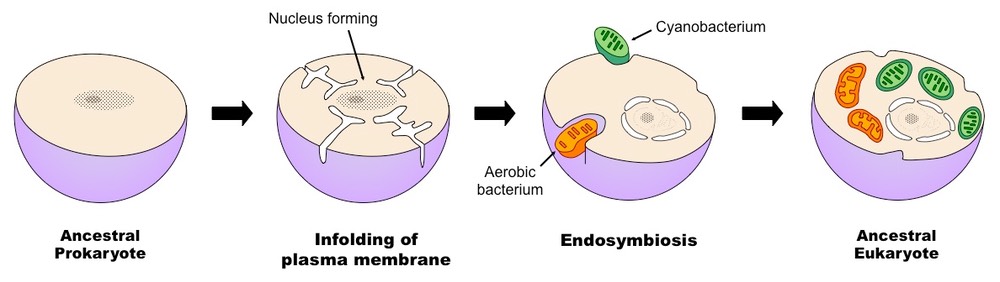
According to this theory these organelles originated as separate prokaryotic organisms which were taken inside the cell as endosymbionts. The theory postulate that an aerobic bacteria established residency within the cytoplasm of a primitive eukaryotic cell. Chloroplasts in a eukaryotic cell have both an inner and outer membrane.
New mitochondria inside eukaryotic cells are produced by. The endosymbiotic theory now generally accepted by biologists concerns the origins of mitochondria and plastids eg. Endosymbiotic theory This theory attempts to explain how eukaryotic cells evolved mitochondria and chloroplasts the r membrane bound-organelles particularly their Answer the following questions 1 W here does the endosymbiotic theory propose as the origin of the mitochondria and chloroplasts found within the modern eukaryotic cel.
1 The endosymbiotic theory is the theory that concerns the origin of eukaryotic cells. In endosymbiotic theory consistent with general evolutionary theory all. It is assumed that the early living forms formed an.
Endosymbiotic theory is the unified and widely accepted theory of how organelles arose in organisms differing prokaryotic organisms from eukaryotic organisms. A theory stating that the eukaryotes evolved through a process whereby different types of free-living prokaryotes became incorporated inside larger prokaryotic cells and eventually developed into mitochondria chloroplasts and possibly other organelles. Chloroplasts which are organelles of eukaryotic cells.
In accordance with the endosymbiotic theory of origin of eukaryotic cells the eukaryotes have evolved from number of cells that happened to join together and form a single eukaryotic cell. In a similar fashion the endosymbiotic uptake of an oxygenic phototrophic prokaryote would have made the primitive eukaryotic photosynthesis. This bacterium would represent the precursor of the present mitochondrion.


0 Comments